Growth for ASEAN+3 was better than expected in 2023, supported by a turnaround in exports amid robust domestic demand and stabilizing economic activities in China. Overall, growth for 2023 was revised upward to 4.4 percent from October’s projection of 4.3 percent. In 2024, growth in the region is forecast to strengthen further to 4.5 percent, anchored by resilient domestic demand and further improvements in trade.
Here are five key takeaways from AMRO’s January 2024 update of the ASEAN+3 Regional Economic Outlook (AREO).
1. Domestic demand continued to underpin growth in the region. Private consumption remained firm, supported by improving labor market conditions and moderating inflation. Retail sales continued to expand, boosted in part by the recovery in travel and tourism. In China, economic activities showed signs of stabilization, with both industrial production and services expanding, and consumer spending remained robust. Additional policy support aimed at enhancing infrastructure investment is poised to further contribute to China’s near-term growth momentum.

2. ASEAN+3 goods exports have been improving. Goods exports have contracted at a slower pace since the second quarter of 2023. The improvement was led by higher exports from Japan and Korea, which benefitted from the rebound in the global chips cycle. On the other hand, exports from ASEAN economies were dampened by lower global commodity prices and subdued demand for non-tech products. Meanwhile, the return of tourism continues to bolster the region’s services exports. ASEAN+3 visitor arrivals returned to around 80 percent of pre-pandemic levels between September and November and is expected to fully recover in 2024.

3. Inflation moderated further in the fourth quarter of 2023 in line with the fall in global commodity prices. Global energy prices continued to trend downwards amid weaker global demand and high inventory levels. The prices of most staple foods, excluding rice, also declined due to bumper crop production. However, core inflation remained elevated for most ASEAN+3 economies due to firm domestic demand.
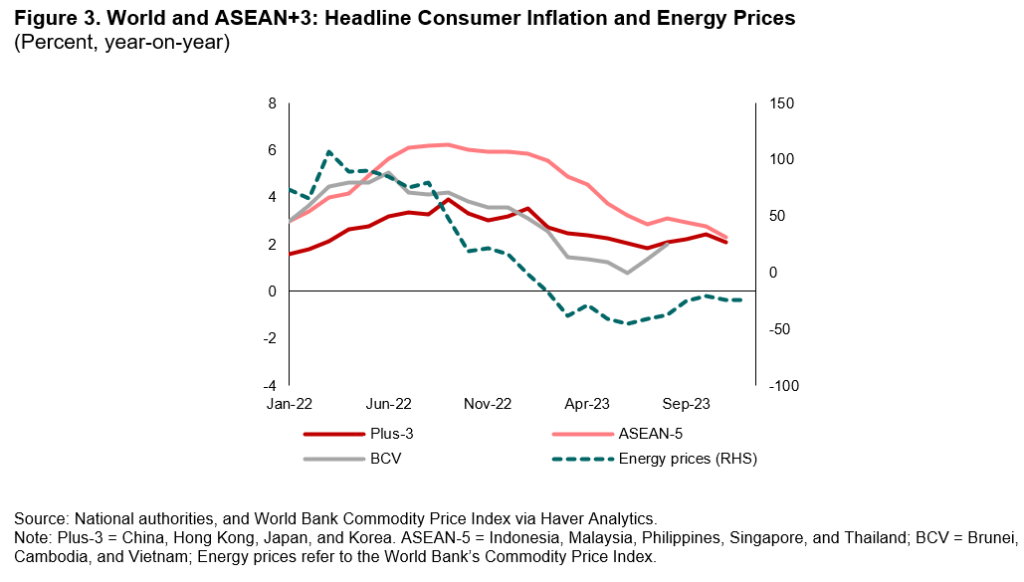
4. Overall, growth for ASEAN+3 is expected to strengthen in 2024. Growth of the region is projected to pick up to 4.5 percent in 2024 from 4.4 percent in 2023 amid improving external demand. The anticipated recovery in China’s property sector and the return of tourism will further support growth in the region. Headline inflation is expected to continue to moderate in 2024, but at a slower pace given the persistently high core inflation in some economies.

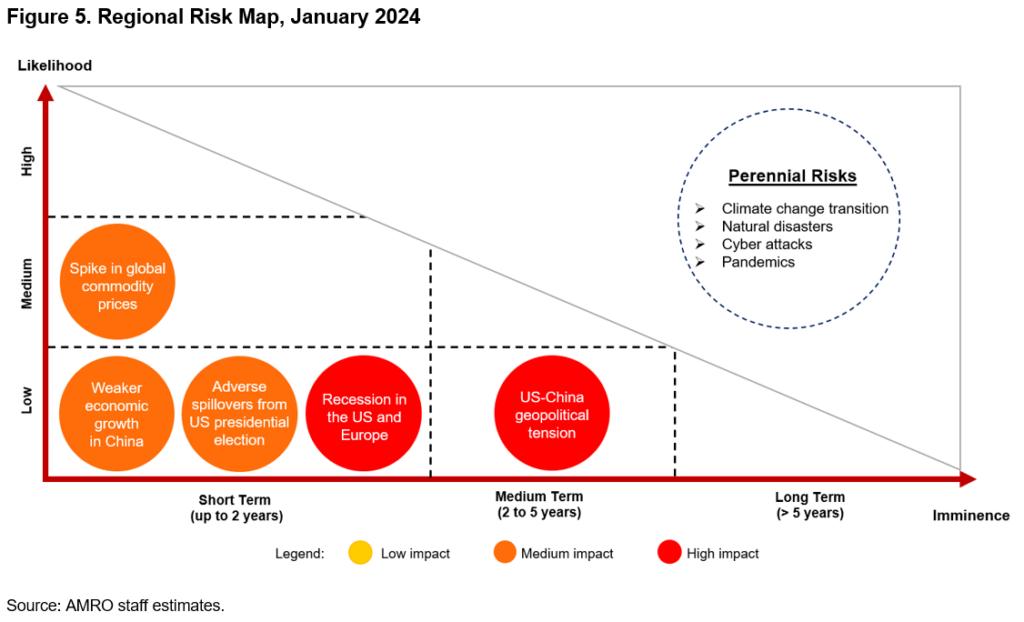
5. The overall balance of risks remains tilted to the downside. Since the October 2023 AREO Update, the risk of financial spillovers from tighter US monetary policy has receded. Instead, adverse spillovers from the run-up to the US presidential election have emerged as a new risk. Heated populist debates during the election campaigns could lead to heightened protectionist measures which may increase financial market volatility. Weaker economic growth in China or a recession in the US and Europe could also weigh on the region’s growth. A more likely risk to the region’s prospects is a spike in global commodity prices, which may be triggered by geopolitical tensions, supply restrictions and/ or El Niño weather conditions. In the longer term, US-China geopolitical tensions remain a risk to the region’s growth prospects.